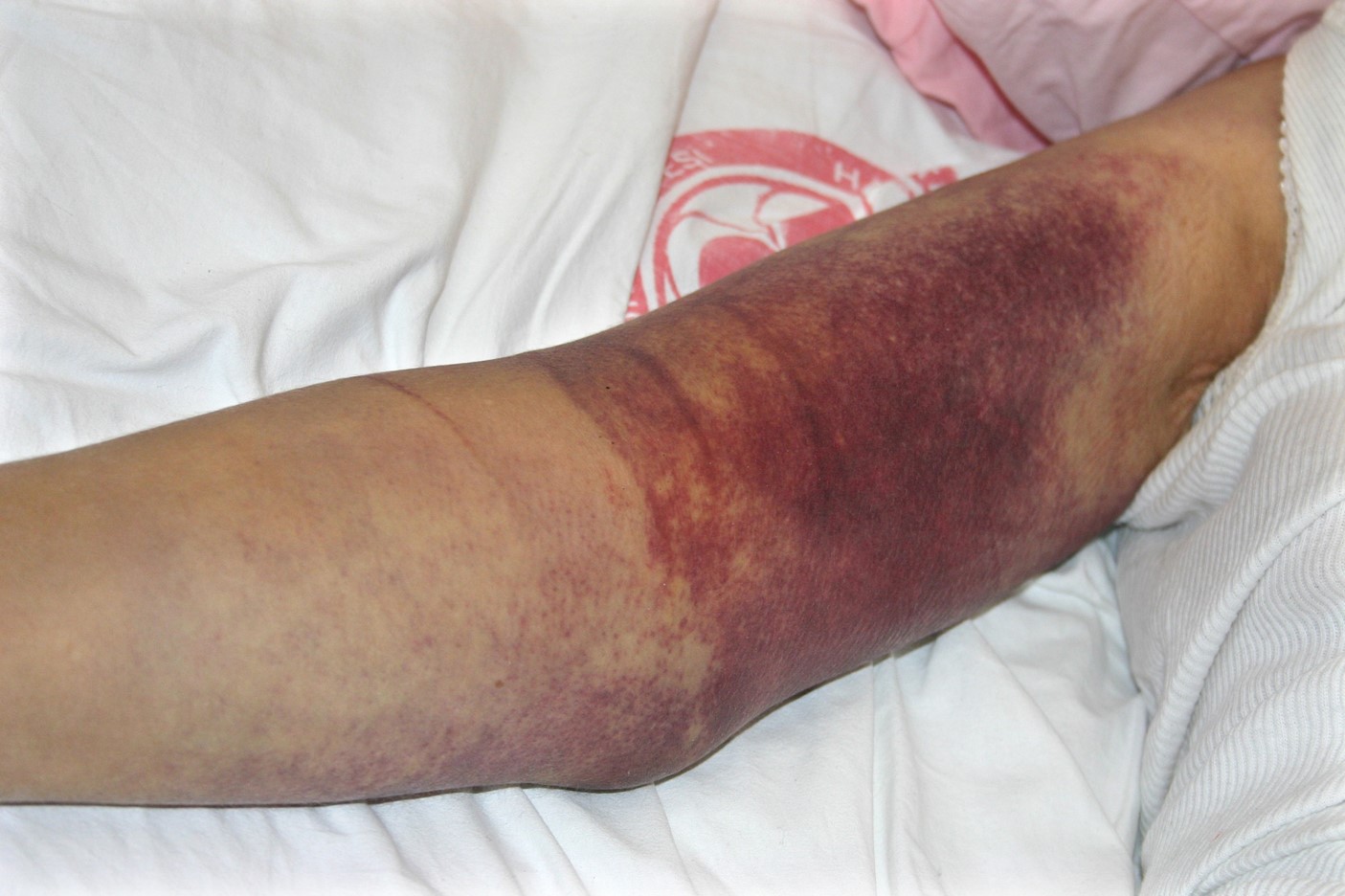
Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) virusis a highly pathogenic viral zoonosis and is the etiological agent of a human disease characterized by fever, severe hemorrhages and death (mortality up to 30%). CCHFV is widely distributed throughout large areas of the world (including several countries in Asia, Middle East, Africa and Europe). The virus is transmitted to humans by ticks and by close contact with infected blood or tissue. To date, there is neither good antiviral nor FDA approved vaccine available for this disease.
The CCHFVaccine project is a six years project, consisting of 14 partners, located in nine different countries from Central Asia, Middle East, Europe and United States. Its general aim is to increase European capacity to control the situation of Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic fever disease on a global basis by developing and deliver a vaccine.
The proposed work program on CCHF virus aims to build a multidisciplinary research network, able to deliver vaccine candidates, methods and procedures eligible for clinical trials, with a special focus on prevention.
|
|
| Large ecchymosis on the forearm of a CCHF patient |